Class 9 NCERT Solutions Geography Chapter 5 - Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
Manage your self-learning with 24/7 online access to NCERT Solutions for CBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife. The chapter solutions cover questions and answers on chapter topics including biosphere reserve, ecosystem, alpine vegetation, deciduous forests etc.
Learn the names of various types of vegetation in India in TopperLearning’s NCERT Solutions for CBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife. For self-study, we also equip you with online practice tests, sample papers, videos and more. For Geography chapter-related doubts, you can share your questions at our website’s ‘UnDoubt’ platform for solutions from experts.
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Exercise 51
Solution 1
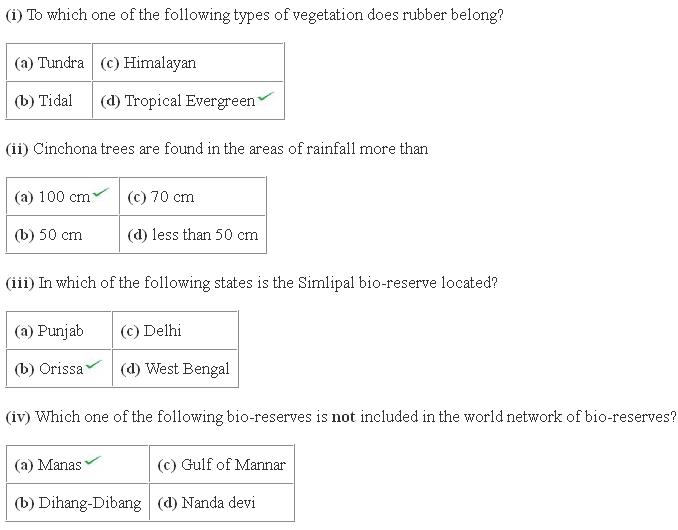
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Exercise 52
Solution 2
(i) Ecosystem -All plants and animals in an area are interdependent and inter-related to each other in their physical environment. This life-supporting system comprising the physical environment i.e. non-living components, like - climate, soil, river etc. along with all organisms living therein, is called an Ecosystem. Human beings also form a part of the ecosystem.
(ii) India is one of the twelve mega bio-diversity countries of the world having a wide variety of plant and animal species.Various factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals (flora and fauna) on the earth and also in India can be listed as below -
- Relief : This includes land, soil type, drainage etc.
- The nature of land influences the type of vegetation. Fertile level land is used for agriculture while grasslands and woodlands are found on undulating and rough terrains.
- Climate which includes temperature, humidity, photoperiod, precipitation etc. are also responsible for the distribution of plants and animals.
- Besides, the nature of plants present in any area determines the animal life of that area.
(iii) A Biosphere Reserve is a large area of protected land for conservation of wild-life, plant and animal resources (especially endangered species of flora and fauna) including micro-organisms. The traditional life of the tribals in their natural habitat is also preserved. A bio-reserve helps to maintain the bio-diversity of the region. The resources of that area are also utilised by the locals in a sustainable manner. It may also contain other protected areas in it. For example, Pachmarhi biosphere reserve consists of one National Park named Satpura and two Wild Life Sanctuaries named Bori and Pachmarhi. Examples of two other bio reserves are – Nilgiris (Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu) and Nanda Devi in Uttarakhand.
(iv)Animals found in Tropical type vegetation : - Elephants, Tigers, Monkeys,etc.
Animals found in Montane type vegetation -Snow Leopard, Kashmir stag, Antelope etc.
Solution 3
(i) Flora refers to the plant kingdom of a particular region.
Fauna refers to the animal life of a particular region.
(ii)
|
Tropical evergreen forests |
Deciduous forests |
|
Tropical evergreen forests are found in the regions which receive more than 200cm of rainfall. |
Deciduous forests are found in the regions which receive rainfall between 200-70 cm. |
|
The trees of the tropical evergreen forests do not shed their leaves at a same time as there is no particular season for shedding their leaves. |
The trees of the deciduous forests shed their leaves for about six to eight months during the dry season. |
|
The tropical evergreen forests are dense. |
These forests are less dense. |
|
These forests are found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, upper parts of Assam and Tamil Nadu and on the western slopes of the western Ghats. |
These forests are found in northeastern states, parts of Central India, West Orissa and Chhattisgarh. |
|
Some of the species of the trees are ebony, mahagony, rosewood and rubber. |
Some of the species of the trees are sandalwood, teak and sal. |
Solution 4
The names of the different types of vegetation found in India are as follows -
Tropical Evergreen or Tropical Rain Forests
Tropical Deciduous Forests
Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
Montane Forests
Mangrove Forests (The Tidal Forests)
The type of vegetation found at high altitudes is Montane Forests. In mountainous areas, the decrease in temperature with increasing altitude results in a succession of natural vegetation belts in the same order as is seen from the tropical to the tundra region.
- From a height of 1000m - 2000m are found the Wet temperate forests .Trees predominant in this area include evergreen broad leaf trees like oaks and chestnuts
- Between 1500m - 3000m are found the temperate forest containing coniferous trees like Pine, Deodar, Silver Fir, Spruce and Cedar. These forests cover mostly the southern slopes of the Himalayas and places with high altitude in southern and north-east India.
- From 3000m - 3600m are the Temperate Grasslands.
- More than 3600m above sea level is the Alpine Vegetation. Silver Fir, Junipers, Pines and Birches are common.
- At higher altitudes, with the approach of the snow line the vegetation gets stunted and shrubs and scrubs merge into the Alpine grasslands.
At still higher altitudes only mosses, lichens and very small shrubs form part of the Tundra type of Vegetation.
Solution 5
Endangered species of plants and animals are those that face the danger of getting extinct. About 1300 plant species and quite a few animal species are endangered and some are extinct. Himalayan wolf, pink headed ducks, Siberian crane, vultures etc are some of the endangered species of animals and birds in India.
The main causes for this endangerment of plant and animal species are as follows:
1. Hunting by greedy hunters for commercial purposes.
2. Pollution due to chemical and industrial wastes, acid deposits etc.
3. Increasing population.
4. Reckless cutting of plants and trees to bring the land under cultivation, expanding industrialization and inhabitation etc.
5. Introduction of alien species.
Excessive exploitation of plants and animals by human beings has resulted in an imbalance in the ecosystem.
Solution 6
India has all the major physical features i.e. topography varying from mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus, islands etc. The different regions of the country have different soil types. Though India has an essentially monsoon type of climate, it has great variations in temperature and humidity across the country. Each of the factors responsible for the diversity in flora and fauna such as land, soil, temperature, photoperiod, precipitation etc. varies across the length and breadth of the country. As a result, which India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna.
