NEET - Chemistry Free Doubts and Solutions
NEET - NEET - Biology - The Living World
What is mean by genus?
NEET - NEET - Chemistry
પાણીના એક નમૂનાનું ca+આયનની સંદ્રતા 0.0002M છે તો તે દ્રાવણમાં ca+ ની સન્દ્રતા વજન કદ થી ppm મા કેટલી થાય
NEET - NEET - Biology - Cell Cycle and Cell Division
why mitosis is called reductional division but binary fission not called reductional division
NEET - NEET - Biology - Reproduction in Organisms
difference between binary fission and mitosis
NEET - NEET - Chemistry - Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry

NEET - NEET - Chemistry
What is the relation between molal elevation constant and molecular elevation constant (In concentration terms) CAN WE WRITE (Molecular elevation constant= 10*Molal elevation constant)??? HERE I AM ASKING ABOUT "ELEVATION'' So pls ans accordingly. If not correct then Pls give the """CORRECT RELATION b/w them"''''
NEET - NEET - Chemistry
What is the relation between molal elevation constant and molecular elevation constant? In concentration term CAN WE WRITE (Molecular elevation constant= 10*Molal elevation constant)???
NEET - NEET - Physics
Respected Sir, Madam Please Physics Subject doubt please clear. For an isotropic solid body, compressibility K =
NEET - NEET - Chemistry
calculate the energy in calories required to produce from neutral he atoms,1 mole of he+ ions using Bohr equation
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
If a particle moving with velocity −4 m/s i^ and acceleration is 2 m/s2i^. What is distance travelled by the paricle in 6 sec.
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
If a particle moving with velocity −4 m/s i^ and acceleration is 2 m/s2i^. What is distance travelled by the paricle in 6 sec.
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
If a particle moving with velocity −4 m/s i^ and acceleration is 2 m/s2i^. What is distance travelled by the paricle in 6 sec.
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
If a particle moving with velocity −4 m/s i^ and acceleration is 2 m/s2i^. What is distance travelled by the paricle in 6 sec.
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
The motion ofbody failing from the rest in resistive medum is described by the equation dvdt=a−bv where a and b are constant. The velocity at any time t is:
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
Acceleration due to gravity at surface of a planet is equal to that at surface of earth and density is 1. 5 times that of earth. If radius of eart is R, radius of planet is
NEET1 - NEET1 - Chemistry
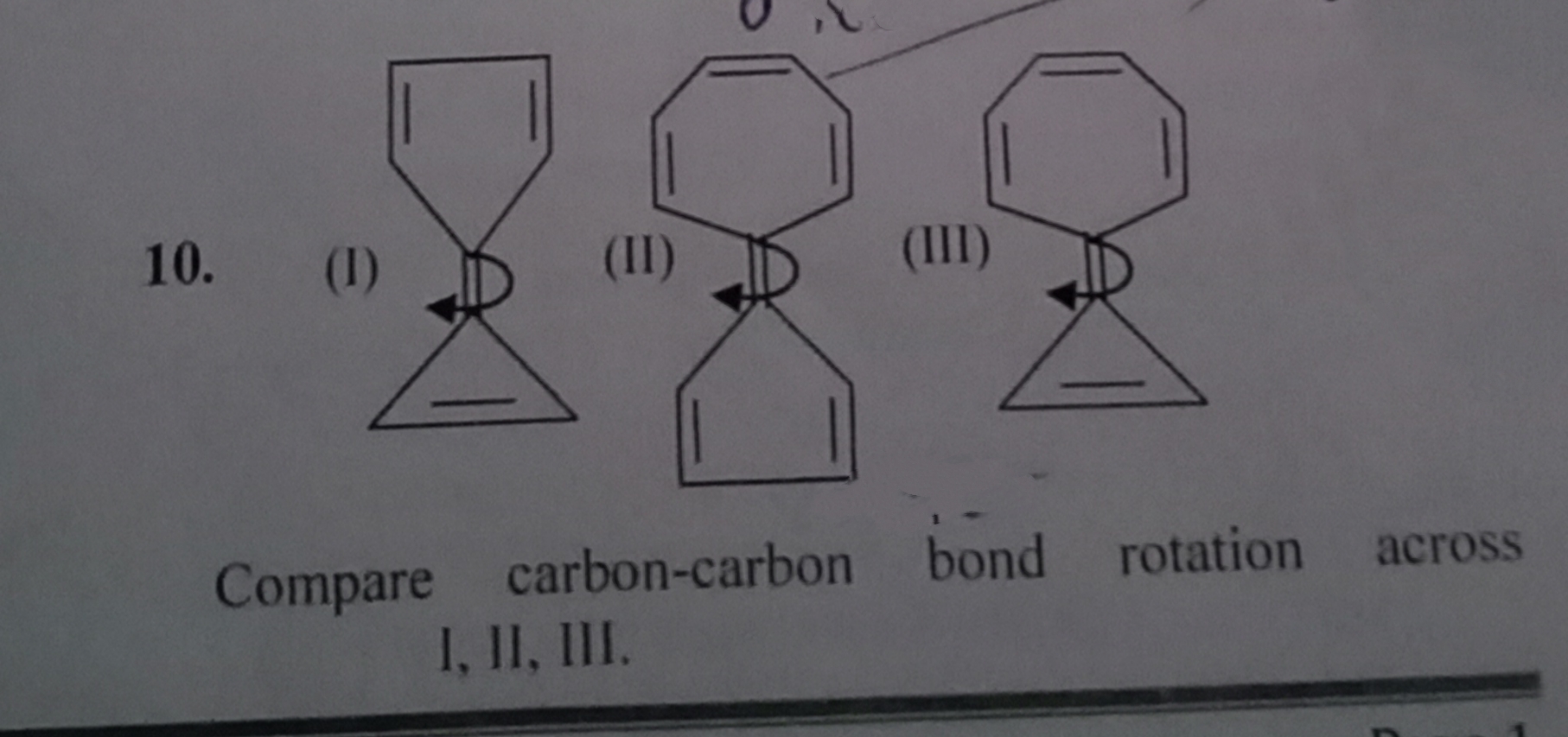
Please answer the following question with explanation

NEET1 - NEET1 - Chemistry
Please answer the following question with explanation
NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
Please answer the following question with explanation

NEET1 - NEET1 - Physics
What is dielectrics and what are its usages
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- 2 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- 3 States of Matter
- 4 Equilibrium
- 5 Hydrogen
- 6 Hydrocarbons
- 7 Environmental Chemistry
- 8 Solutions
- 9 Chemical Kinetics
- 10 Surface Chemistry
- 11 Biomolecules
- 12 Polymers
- 13 Chemistry in Everyday Life
- 14 Atomic Structure
- 15 Chemical Thermodynamics
- 16 Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- 17 p-Block Elements
- 18 d - and f - Block Elements
- 19 Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- 20 Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- 21 Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- 22 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- 23 Co-ordination Compounds
- 24 Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- 25 s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- 26 Solid State
- 27 Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- 28 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- 29 Principles Related to Practical Chemistry